What is the significance of this?
- Serverless Architecture: A fully serverless resume website showcasing modern cloud-native development practices
- Infrastructure as Code: Complete AWS infrastructure managed through Terraform with automated deployments
- CI/CD Pipeline: GitHub Actions automation for one-click deployments with visitor counter functionality
- Local Development: LocalStack integration for local AWS development without cloud costs
- Professional Portfolio: Demonstrates SRE/DevOps expertise through the project itself
How is automation accomplished?
- Terraform Infrastructure: Complete AWS infrastructure provisioned as code including S3, CloudFront, Lambda, DynamoDB, and API Gateway
- GitHub Actions CI/CD: Automated deployment pipeline that builds, tests, and deploys on every commit
- Serverless Backend: Python Lambda function with DynamoDB for visitor counter with CORS support
- Static Website Hosting: S3 + CloudFront for global CDN with automatic HTTPS and custom domain support
- LocalStack Development: Local AWS environment for development and testing without cloud costs
- Infrastructure Monitoring: CloudWatch logs and metrics for observability and debugging
Prerequisites
- AWS account with programmatic access
- AWS IAM user with the following policies:
AmazonS3FullAccessCloudFrontFullAccessAWSLambdaFullAccessAmazonDynamoDBFullAccessAmazonAPIGatewayAdministratorIAMFullAccessCloudWatchLogsFullAccess
- Terraform >= 1.0
- Docker (for LocalStack development)
- Git and GitHub account
Source Code
https://github.com/Lforlinux/Cloud-CV
How to deploy the infrastructure
Automated Deployment (Recommended)
The project uses GitHub Actions for one-click deployment:
- Fork the repository to your GitHub account
- Configure AWS Secrets in GitHub repository settings:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
- Push to main branch - GitHub Actions will automatically deploy
- Access your Cloud CV via the CloudFront URL provided in the deployment logs
Manual Deployment
|
|
Architecture
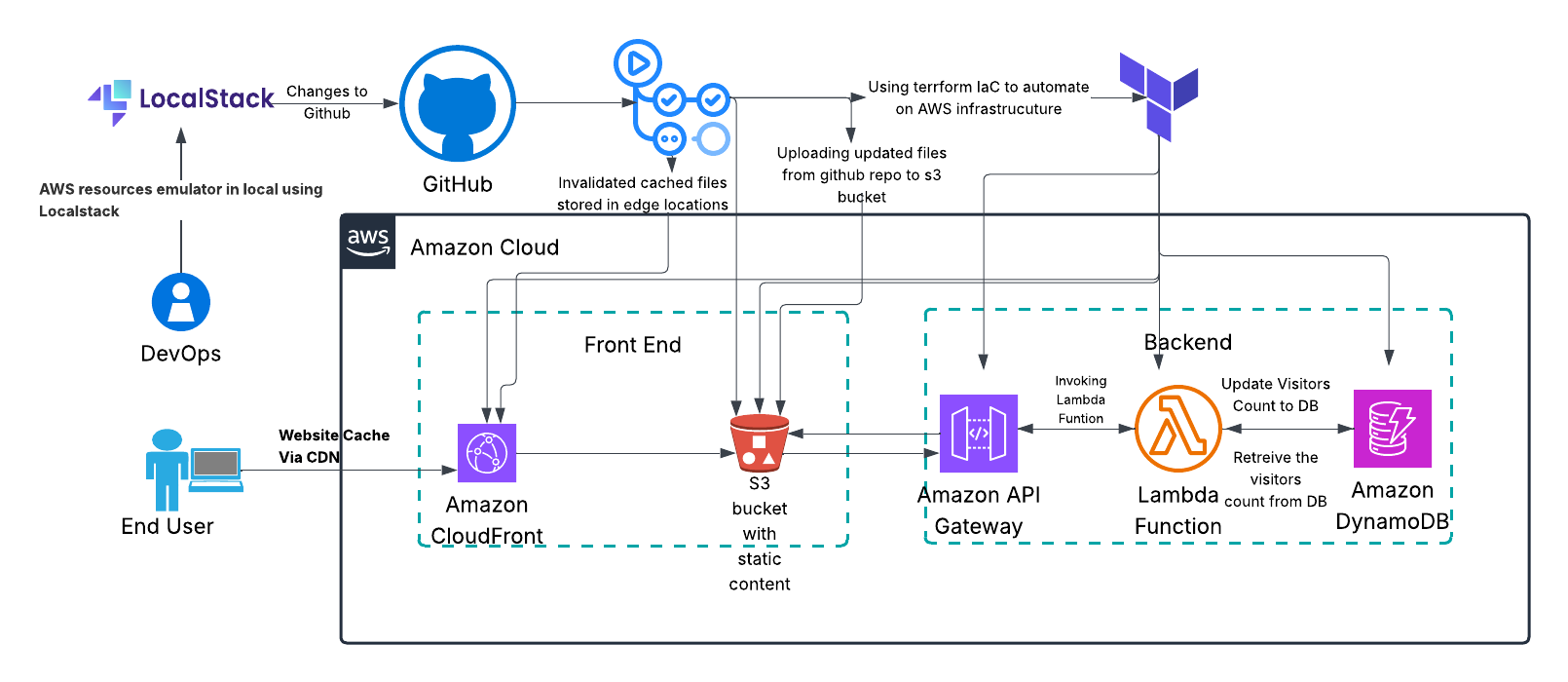
Core Components
- S3 Bucket: Static website hosting with versioning and encryption
- CloudFront CDN: Global content delivery with custom domain support
- Lambda Function: Serverless visitor counter with DynamoDB integration
- DynamoDB: NoSQL database for visitor count storage
- API Gateway: RESTful API with CORS support for frontend integration
- CloudWatch: Logging and monitoring for observability
Local Development with LocalStack
Start LocalStack Environment
|
|
Access Local Development
- Website: http://localhost:4566/cloud-cv-local/index.html
- S3 Browser: http://localhost:4566/cloud-cv-local/
- LocalStack Health: http://localhost:4566/_localstack/health
Project Architecture & Implementation
Technical Implementation
This Cloud CV project demonstrates a complete serverless architecture built with modern DevOps practices:
- Frontend: Static HTML/CSS/JavaScript hosted on S3
- Backend: Python Lambda function for visitor counter
- Database: DynamoDB for storing visitor statistics
- CDN: CloudFront for global content delivery
- Infrastructure: Terraform for Infrastructure as Code
- CI/CD: GitHub Actions for automated deployments
Visitor Counter Implementation
Backend (Lambda + DynamoDB)
|
|
Frontend Integration
|
|
CI/CD Pipeline Features
GitHub Actions Workflow
- Terraform Deployment: Automated infrastructure provisioning
- File Upload: Automatic S3 upload with correct content types
- Cache Invalidation: CloudFront cache invalidation for immediate updates
- Health Checks: Deployment verification and status reporting
Deployment Triggers
- Push to main: Automatic production deployment
- Pull Requests: Infrastructure validation and testing
- Manual Dispatch: On-demand deployment capability
Monitoring and Observability
CloudWatch Integration
- Lambda Logs: Function execution logs and errors
- DynamoDB Metrics: Database performance and usage
- CloudFront Analytics: CDN performance and cache hit rates
- API Gateway Logs: API request/response monitoring
Cost Optimization
- S3 Intelligent Tiering: Automatic cost optimization for storage
- CloudFront Caching: Reduced origin requests and costs
- Lambda Pay-per-Use: Serverless scaling with no idle costs
- DynamoDB On-Demand: Pay only for actual usage
Security Best Practices
Infrastructure Security
- S3 Bucket Policies: Restrictive access controls
- CloudFront OAC: Secure origin access control
- Lambda IAM Roles: Least privilege access
- API Gateway CORS: Controlled cross-origin access
Data Protection
- S3 Encryption: Server-side encryption for all objects
- DynamoDB Encryption: Encryption at rest and in transit
- HTTPS Only: CloudFront enforces secure connections
- No Sensitive Data: No personal information stored in visitor counter
Performance Optimization
CDN Optimization
- CloudFront Caching: Global edge locations for fast delivery
- Compression: Automatic gzip compression for text files
- Cache Headers: Optimized cache policies for different content types
- HTTP/2: Modern protocol support for better performance
Lambda Optimization
- Cold Start Mitigation: Optimized function initialization
- Memory Tuning: Right-sized memory allocation
- Connection Reuse: DynamoDB connection pooling
- Error Handling: Robust error handling and retries
Future Enhancements
Planned Features
- Multi-Environment Support: Staging and production environments
- Custom Analytics: Advanced visitor tracking and analytics
- A/B Testing: Content variation testing capabilities
- Multi-Language Support: Internationalization features
Technical Improvements
- GitOps Integration: ArgoCD for GitOps workflows
- Infrastructure Testing: Terratest for infrastructure validation
- Security Scanning: Automated security vulnerability scanning
- Performance Testing: Load testing with Artillery or K6
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- CloudFront Cache: Use cache invalidation for immediate updates
- CORS Errors: Ensure API Gateway CORS configuration
- Lambda Timeouts: Check DynamoDB permissions and connectivity
- S3 Access: Verify bucket policies and CloudFront OAC
Debug Commands
|
|
Contributing
Development Setup
- Fork the repository
- Create feature branch:
git checkout -b feature/your-feature - Make changes and test locally with LocalStack
- Commit changes:
git commit -m "Add your feature" - Push to branch:
git push origin feature/your-feature - Create Pull Request
Code Standards
- Terraform: Follow HashiCorp best practices
- Python: PEP 8 style guide compliance
- JavaScript: ESLint configuration
- Documentation: Clear and comprehensive README updates
Conclusion
This Cloud CV project demonstrates modern cloud-native development practices, showcasing:
- Infrastructure as Code with Terraform
- Serverless Architecture with AWS Lambda and DynamoDB
- CI/CD Automation with GitHub Actions
- Local Development with LocalStack
- Professional Portfolio that showcases itself
The project serves as both a functional resume website and a comprehensive example of DevOps/SRE best practices, making it an excellent addition to any cloud engineer’s portfolio.
Live Demo: Cloud-CV
Source Code: https://github.com/Lforlinux/Cloud-CV
